Subversion (SVN) Hosting and Management: Configuration, Modernization, and Support
The digital backbone of most modern enterprises relies heavily on robust control over their evolving codebase. While the software development landscape has seen the rise of various version control systems, one of the foundational technologies, Subversion (or SVN), continues to be used extensively, especially within large organizations with long-standing projects.
As a highly reliable and mature centralized version control system, SVN offers unique advantages in certain corporate environments, particularly where strict access control and simple workflows are prioritized. According to historical data, SVN adoption peaked in the late 2000s, establishing a massive footprint that many legacy systems still rely on today, representing a significant portion of the world's commercial source code.
This article delves into the configuration, management, and essential modernization strategies for the svn version control system, ensuring that organizations can maintain the stability of their existing infrastructure while adopting modern development practices. We will explore how SVN works, how to set up a secure SVN server, detail essential team collaboration with SVN workflows, and show how platforms like RhodeCode provide the definitive solutions for bridging the gap between legacy SVN and modern distributed version control software like Git.
Why do enterprises continue to rely on Subversion (SVN)?
Despite the increased popularity of distributed control systems, many large enterprises still find compelling reasons to stick with Subversion VCS. Its maturity, simplicity, and proven stability are key factors. For teams handling massive files (often used in industries like gaming, CAD, or embedded software) or specific project types, the centralized nature of SVN - where storing code history happens on a single, authoritative SVN repository - offers straightforward management and strict SVN access control.
The architecture of SVN simplifies operations like initial checkout and SVN change synchronization. Furthermore, for organizations where regulatory compliance is paramount, the centralized log and rigid permission system of SVN provide an easier path for auditing and code revision tracking. This reliability and proven track record in complex enterprise environments ensure SVN remains a critical component of their source control infrastructure, providing robust development support for years to come. Many users find its model easier to grasp than that of distributed systems, making the learning curve for new users minimal.
Understanding Centralized Version Control: How SVN works
To effectively manage an svn version control system, it is critical to understand the underlying principles of its centralized version control system architecture. Unlike Git, where every developer has a full copy of the SVN repository history, SVN operates by has a single, authoritative remote SVN repository access point. Developers checkout a working copy, make changes, and then commit those changes back to the central server.

This model provides clear control over the source of truth. SVN tracks changes by revision number, allowing for precise code versioning and the ability to easily revert files or entire project systems to a previous state. Understanding how SVN works is foundational for leveraging its strengths in team collaboration with SVN and effectively managing project versions in SVN.
How to set up a secure SVN repository server
The foundation of any successful SVN implementation is a securely configured SVN server setup. A key question is, "What steps are needed to set up a secure SVN repository server?" The process involves selecting the appropriate server software (often Apache with the mod_dav_svn module or the dedicated svnserve server), configuring network access control, and establishing user authentication.
For enterprise use, integrating the SVN server with an existing directory system (like LDAP or Active Directory) is a top priority for centralized user management. The SVN repository itself should be placed in a protected location, and Subversion access control rules must be meticulously defined, often used path-based authorization files, to restrict who can read and write source files. Proper configuration ensures that storing code history remains safe from unauthorized changes.
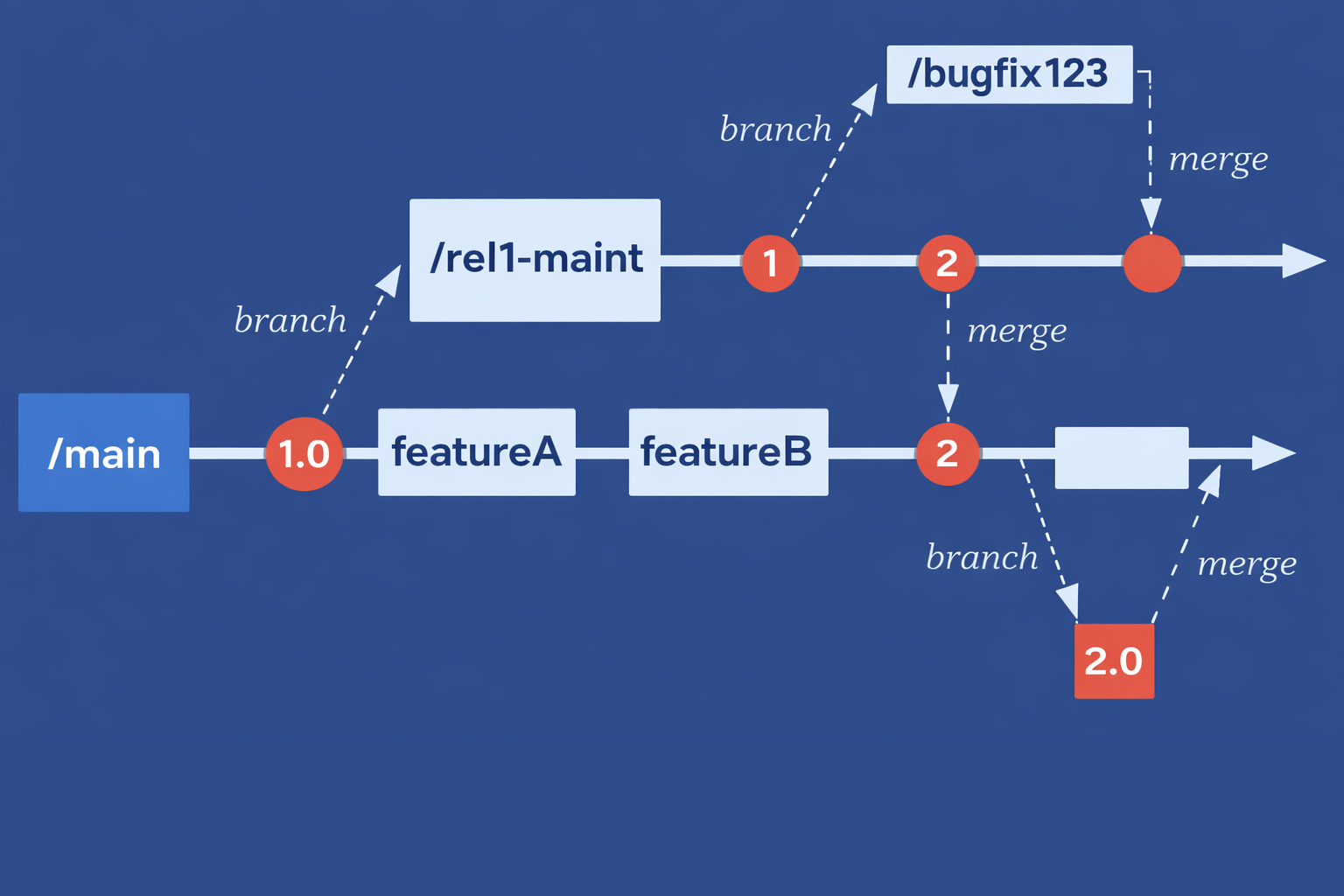
Managing standard directory structures: Trunk, Branches, and Tags
For efficient team collaboration with SVN, a standardized directory structure is essential. "What is the standard directory structure used in SVN?" SVN typically organizes an SVN repository into three main directories, which is a key practice for managing project versions in SVN:
- Trunk. This directory holds the main line of development. Most users will commit their daily changes here.
- Branches. These are copies of the Trunk (or another branch) used for isolated development efforts, such as new features or major fixes. The SVN merge command is used to integrate changes back.
- Tags. These are immutable copies of the code at a specific point in time, typically marking stable releases.
This SVN trunk, branches, tags structure is a best practice, ensuring clarity and order for code versioning. Experts recommend treating Tags as read-only to guarantee the integrity of release points.
Locking mechanisms and conflict resolution in SVN
In a centralized version control system, managing concurrent changes to the same files is a key concern. "How does SVN handle concurrent modifications and conflict resolution?" SVN offers a top-tier "copy-modify-merge" model by default. Users make changes locally and then updating their working copy before attempting to commit.
If a conflict occurs during the commit, Subversion marks the conflicted files with standard conflict markers, and the developer used a manual process to resolve the difference before a final commit. File-locking, while supported for binary files (e.g., image or data files) to prevent un-mergeable changes, is most often discouraged for source code as it can impede collaborative development.
Best practices for committing and updating in a centralized environment
Adhering to best practices optimizes team collaboration with SVN. "What are the best practices for committing and updating using SVN commands?" Users should aim for atomic commits—each commit should represent a single, complete logical change. Before any commit, developers should always update their working copy with the latest changes from the SVN repository used the svn update command to minimize potential merge conflicts and ensure effective SVN change synchronization. Clear, descriptive commit messages are vital for code revision tracking and provide valuable context for other users used the system. A good practice is to always perform a pre-commit check to ensure files compile correctly.
Essential SVN Workflows for Enterprise Teams
Effective team collaboration with Subversion requires established workflows that leverage the system's strengths. These workflows define how SVN works in practice, guiding developers on tasks like feature development and bug fixing. A common enterprise workflow involves:
- Checkout the Trunk.
- Create a feature branch (using svn copy trunk branches/feature_name).
- Work and commit small, logical changes to the feature branch.
- Regularly merge Trunk changes into the feature branch (svn merge trunk).
- Perform final quality assurance and code review.
- Merge the completed feature branch back into the Trunk (svn merge --reintegrate).
This structured approach, supported by essential SVN commands: checkout, commit, update, is crucial for large teams used a centralized version control system.
Modernizing Legacy SVN with RhodeCode
Many organizations face the challenge of modernizing their legacy Subversion infrastructure without disrupting critical operations. RhodeCode provides a powerful solutions platform that acts as a unified interface for all major version control software, including SVN. This allows enterprises to inject modern workflows and enterprise-grade services into their existing Subversion VCS, maximizing the longevity and control over their valuable data. RhodeCode ensures that SVN hosting is not just stable, but also feature-rich and aligned with current development practices. This approach drastically reduces the total cost of ownership (TCO) associated with managing disparate tools.
Bringing "Pull Request" style Code Reviews to SVN
One of the most significant gaps between traditional Subversion and modern distributed systems is the lack of native "pull request" style code reviews. "Can I implement modern code review practices with my existing SVN code?" Yes. RhodeCode allows users to create and manage sophisticated code reviews for SVN changes directly through its interface. This brings crucial quality control and enhanced team collaboration with SVN features, allowing for pre-merge review of changes before they are finalized with an SVN commit. This feature is essential for enterprises looking to improve their development lifecycle and reduce the risk of integrating faulty source code.
Implementing Granular Permission Management for SVN
While SVN has its own authz access control list mechanisms, managing them across dozens or hundreds of SVN repository systems can become cumbersome. "How can I achieve centralized, granular permission control for all my SVN repositories?" RhodeCode offers a consolidated permission system that applies across SVN, Git, and Mercurial. This allows administrators to implement detailed SVN access control—down to the branch or files level—from a single dashboard, simplifying compliance and enhancing security. This centralized control is especially beneficial for large-scale software development where numerous users require specific rights.
Auditing and Compliance: Tracking every SVN interaction
For highly regulated industries (e.g., finance, healthcare), robust auditing is non-negotiable. "How can I ensure comprehensive auditing and compliance for every SVN interaction?" RhodeCode automatically logs and tracks every SVN operation—from a checkout to a commit—providing a complete and immutable audit trail. This feature is vital for meeting stringent regulatory compliance requirements (like SOX or ISO standards) and provides an unparalleled level of control over source data. The software's detailed reporting services allow customer support to quickly identify and track all code revision tracking events.
The RhodeCode Advantage: Seamless SVN to Git Migration
While modernization can extend the life of Subversion, many organizations eventually plan a full migration to a distributed system. RhodeCode offers a strategic advantage by not forcing an immediate, disruptive transition. Instead, it provides a unified platform to manage both, enabling a phased, low-risk shift. This minimizes the risk associated with a large-scale change of the core version control software.
How to run SVN and Git side-by-side on a single platform
"Can our team use both SVN and Git concurrently on the same source code?" With RhodeCode, the answer is a resounding yes. RhodeCode allows users to interact with the same underlying source files used either SVN or Git tools (or both). This means part of the team can start development used Git workflows, while other parts continue with their familiar Subversion practices. This capability is most valuable for managing legacy projects alongside new development, providing true flexibility in code versioning and SVN change synchronization. RhodeCode facilitates the gradual shift, supporting both systems until the organization is fully ready to transition away from Subversion VCS. This hybrid approach is a top consideration for modern enterprises.
The svn version control system remains a powerhouse for many enterprise development environments, offering mature, stable services. However, its longevity hinges on the ability to integrate modern workflows and tools. RhodeCode offers the top solutions for maintaining, modernizing, and eventually migrating your Subversion assets. By leveraging RhodeCode unified platform, you gain advanced security, robust auditing, and modern team collaboration with SVN features, extending your control and ensuring your source code data is secure.
Ready to bring enterprise-grade features and seamless Git compatibility to your Subversion VCS? Explore the RhodeCode platform today to modernize your SVN hosting and management.