Mercurial (Hg) SCM: Scalable Configuration Management and Collaboration
The Mercurial version control system (often referred to as Hg) stands as a powerful and elegant choice in the world of distributed configuration management. While Git often dominates the conversation, Mercurial offers a distinct set of advantages, particularly for enterprise environments that prioritize usability, performance on large codebases, and maintainable history. This deep dive explores the core mechanics of Mercurial, contrasting it with competitors and highlighting how platforms like RhodeCode transform Hg into a powerhouse for professional development teams.
The Business Case for Mercurial: Performance and Usability
For organizations seeking a robust and highly efficient solution for managing its codebase, Mercurial presents a compelling business case. Its design philosophy centers on simplicity, speed, and reliability. Mercurial is well-known for being exceptionally fast, especially when handling large repositories with extensive file history. Its architecture ensures that common operations, such as cloning, committing, and browsing changes, are remarkably quick.
One of the key selling points of Mercurial is its beginner-friendly nature. Its command set is intuitive and consistent, making it easier for new developers to grasp the fundamental concepts quickly. This focus on usability reduces the learning curve and ensures higher team productivity from the outset. Furthermore, Mercurial's robust merging capabilities handle complex conflicts with greater grace than many other systems, contributing to smoother collaborative development. What is Mercurial at its heart? It is a lightweight yet powerful distributed system designed for scale and clarity.
Mercurial vs. Git: Choosing the right Distributed VCS
When deciding on a version control system, teams often find themselves weighing the pros and cons of Mercurial vs Git. Both are distributed systems, meaning every developer has a full copy of the project history, ensuring resilience and offline work capability. However, their internal does differ significantly.
Mercurial prioritizes a simpler, linear history. Its approach to changes is generally less flexible than Git's but provides a more predictable and auditable trail, which is crucial for regulated industries. Git does offer more ways to rewrite history, making it popular for rapid, smaller projects, but this complexity can introduce risk and confusion within large team environments.
Mercurial also shines in managing binary files and large repositories due to its extensions, like the Largefiles extension, which efficiently track these assets without bloating the core repository. For many large enterprise projects, the stability and clarity of Mercurial's history and its ease of merging make it the superior choice.
Core Concepts of Mercurial for Developers
To understand how Mercurial works, it is essential to grasp its foundational concepts. Mercurial operates on simple, clear principles that make it a favorite among developers. This section serves as a brief Mercurial tutorial for beginners.
Сreating a Mercurial repository and basic commands
Starting a new project with Mercurial is straightforward. The Mercurial commands guide begins with hg init to create a new Mercurial repository. To track files, you use hg add, and to commit changes to its local history, you use hg commit. The simplicity of its core control commands ensures a fast onboarding process for any developer. Its simplicity does not compromise its power.
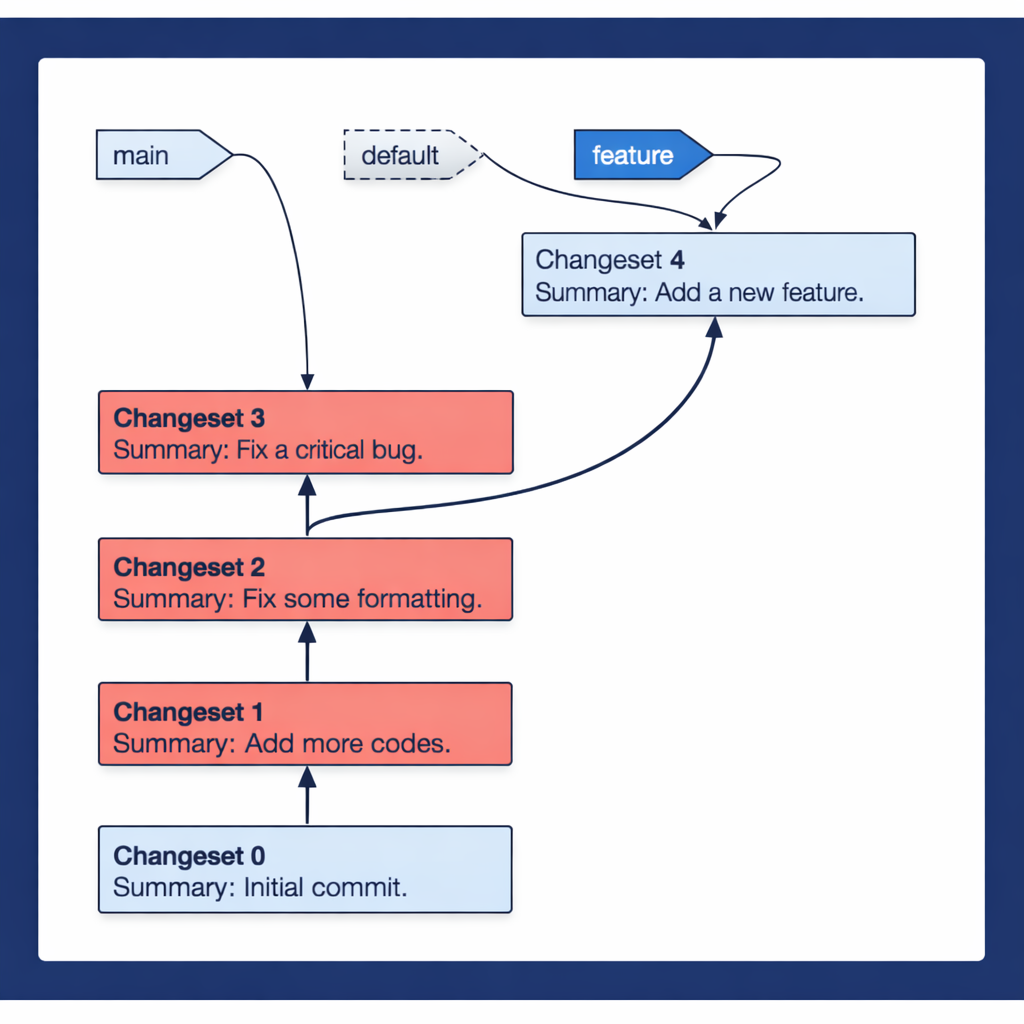
Understanding Changesets and Heads in Mercurial
The fundamental unit of history in Mercurial is the changeset. A changeset is an atomic unit representing a set of changes along with a unique ID, author, and timestamp. Unlike Git's SHA-1 hashes, Mercurial uses an efficient manifest-based structure. Heads are the latest changesets on any branch within the repository. Mercurial supports multiple heads on a branch, which often occur after a pull operation, necessitating a merging operation to resolve conflicts. This transparent mechanism ensures all developers are aware of the pending changes.
Branching and Bookmark workflows in Hg
Mercurial branching and merging is implemented in a few elegant ways. Named Branches are permanent branches recorded in the repository history, ideal for long-term development lines. More frequently, developers use Bookmarks and Phases. Bookmarks are lightweight pointers, similar to Git branches, perfect for feature development and temporary lines of work. Phases (public, draft, secret) control the mutability of changesets, promoting good team collaboration and ensuring stable, shared history.
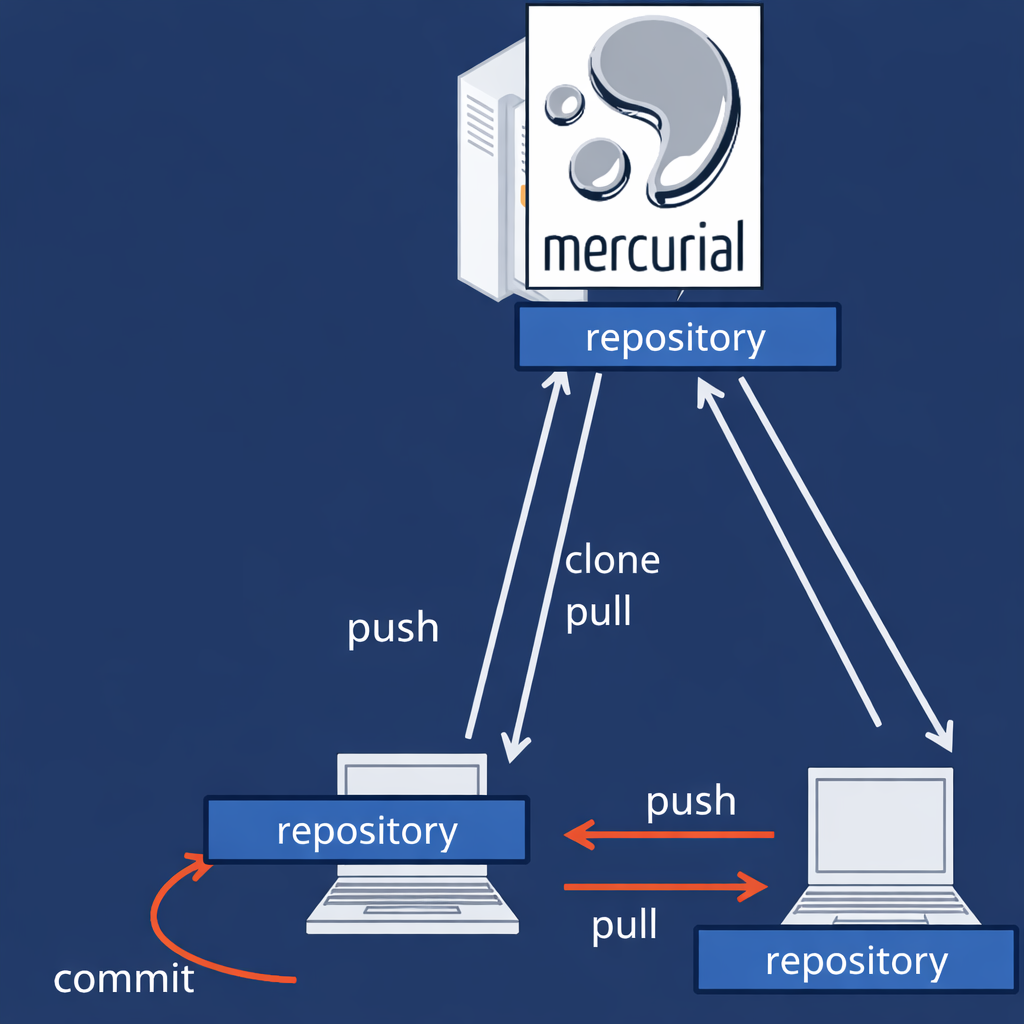
Synchronization: Push, Pull, and Update operations
The distributed nature of Mercurial is realized through its synchronization commands. hg pull retrieves changes from a remote repository, merging them into the local repository if possible (or making a new head if conflicts arise). hg push sends local changes to a remote repository. Finally, hg update changes the working copy to reflect a specific changeset or branch head. This clear separation of concerns ensures that a developer does not accidentally corrupt their local working project.
RhodeCode: The Premier Platform for Mercurial Enterprise Management
While Mercurial is powerful on its own, enterprise-grade projects require a platform that adds centralized control, security, and advanced collaboration features. This is where RhodeCode enters the picture, transforming Mercurial into a fully compliant, secure, and scalable enterprise solution. RhodeCode provides a unified interface for managing multiple Mercurial repositories, greatly enhancing the speed and accountability of the development process. Its robust set of features ensures that large, complex projects can be managed with ease.
Handling large repositories and binary files with Mercurial
For large organizations, managing vast repositories and dealing with large binary assets is a constant challenge. RhodeCode provides first-class support for Mercurial's Largefiles extension, optimizing the storage and retrieval of assets that don't benefit from standard delta compression. This integration ensures that checkout and update speed remains high, even for projects containing GBs of binary data.
Advanced Code Review features for Mercurial projects
High-quality code requires rigorous review. RhodeCode elevates Mercurial projects by providing sophisticated, in-browser code review tools. These features allow developers and team leads to comment directly on changesets and individual lines of code, making the review process highly efficient and providing clear accountability for all changes. Its system does not enforce any specific workflow but facilitates all common Mercurial best practices.
Centralized permission control for distributed Hg teams
In a distributed system, centralized access control is paramount for security. RhodeCode offers granular, centralized permission control over all Mercurial repositories, integrating with enterprise identity management systems. This ensures that only authorized developers have access to sensitive projects and that all actions are tracked, making accountability a key feature of the platform. RhodeCode ensures that the benefits of a distributed system are achieved without sacrificing security control.
Unified Workflow: Managing Mercurial alongside Git and SVN in RhodeCode
Many organizations inherit or acquire multiple version control systems. A distinct advantage of the RhodeCode platform is its ability to unify managing Mercurial alongside Git and Subversion (SVN) repositories under a single interface. This allows team members to work on different projects using their preferred or required system without needing to switch tools or learn new interfaces. RhodeCode abstracts the control layer, providing a consistent code review, access control, and history view across all technologies. This flexibility greatly benefits large development team environments and ensures maximum speed and efficiency in cross-project collaboration.
The Mercurial version control system remains a top-tier choice for professional development. Its commitment to simplicity, speed, and clear history does translate directly into higher team productivity and reduced operational overhead.
Ready to harness the full power of Mercurial for your enterprise? Discover how RhodeCode provides the advanced features, security, and unified control needed to scale your Mercurial projects efficiently. Start your free trial today and revolutionize your development system workflow.