Why Python is the Best Computer Language for Modern Development
Python has consistently held its ground as a leading computer language, but in 2026, its prominence has reached new heights. What makes Python so incredibly powerful and versatile?
From web development to artificial intelligence, elegant syntax and extensive libraries make it the go-to choice for a vast array of applications. Its readability and active community support mean that both beginners and seasoned professionals find it an indispensable tool. This section explores the fundamental reasons behind Python's enduring appeal and why it continues to be a driving force in the tech world.
Python's open-source nature, coupled with its cross-platform compatibility, makes it an ideal choice for diverse projects. Developers can write code once and deploy it across different operating systems, significantly reducing development time and effort. Furthermore, the constant evolution of the ecosystem, driven by a global community, ensures that the language remains at the forefront of technological advancements, constantly integrating new features and optimizations.
What are the Key Features and Benefits of Python for Developers?
Python's feature set is one of its strongest assets. It's an interpreted, object-oriented, high-level programming language with dynamic semantics. This combination allows for rapid application development and makes it very attractive for scripting and connecting existing components.
Here are some of the core features and benefits that set Python apart:
- Simplicity and Readability. Python's syntax is designed to be clear and intuitive, resembling natural language. This significantly reduces the learning curve, making "python for beginners" an accessible journey.
- Extensive Standard Library. Python boasts a vast collection of modules and packages, providing ready-to-use solutions for everything from web protocols to operating system interfaces. This rich library accelerates development and reduces the need to write code from scratch.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility. Python code runs seamlessly on various operating systems like Windows, macOS, and Linux, ensuring broad applicability for projects.
- Large and Active Community. A thriving global community contributes to Python's growth, offering extensive documentation, tutorials, and support for developers facing challenges.
- Versatility. As a general-purpose language, Python excels in diverse domains, including web development, data analysis, machine learning, and automation.
The ability to integrate easily with other languages like C/C++ also expands its utility, allowing developers to leverage existing codebases and optimize performance-critical sections.
How to Get Started with Python for Beginners: A Practical Guide
Embarking on your journey with the "python programming language" is easier than you might think. This practical guide will walk you through the essential steps to set up your environment and execute your first Python commands.
Step-by-Step Python Installation and Setup
- Download. Visit the official Python website (python.org) and download the latest stable version for your operating system.
- Run the Installer. Follow the on-screen instructions. Important: Make sure to check the box that says "Add Python X.Y to PATH" during installation. This allows you to run Python commands from any directory in your terminal.
- Verify Installation. Open your terminal or command prompt and type python --version or python3 --version. You should see the installed Python version.
- Install a Code Editor. While you can use a basic text editor, an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) or a specialized code editor like VS Code, PyCharm, or Sublime Text will greatly enhance your coding experience with features like syntax highlighting and debugging.
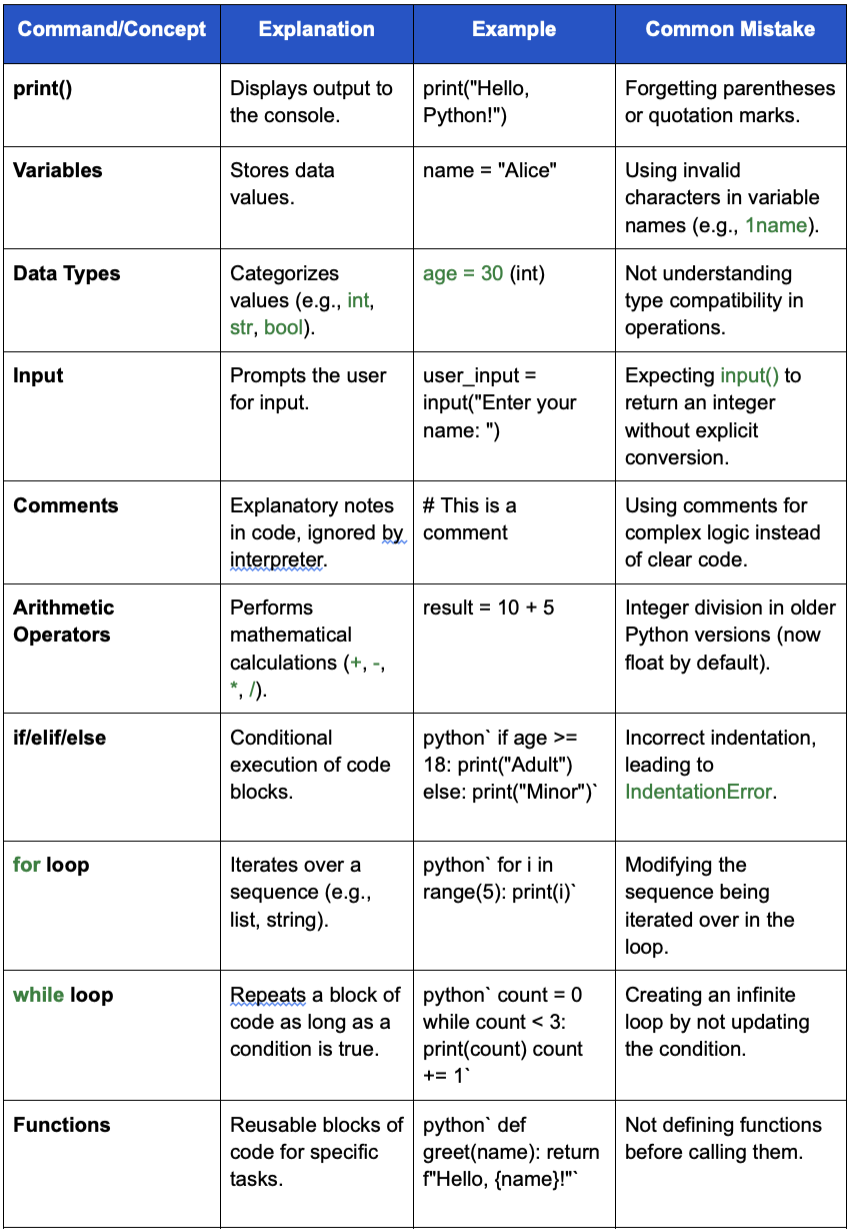
Essential Python Commands for Basic Scenarios
Here's a structured list of fundamental Python commands, complete with explanations, examples, and common pitfalls.
Interesting Fact
Did you know that the "python programming language" was named after the British comedy group Monty Python, not the snake? Guido van Rossum, Python's creator, was a big fan of "Monty Python's Flying Circus" and wanted a short, unique, and slightly mysterious name for his new language.
Python Computer Language Examples: Real-World Applications
"What is python used for?" This question uncovers the incredible breadth of Python's utility. Its adaptability allows it to be a dominant force in several rapidly evolving fields.
- Web Development. Frameworks like Django and Flask make Python a formidable tool for building robust and scalable web applications. Many popular websites and services rely on Python for their backend infrastructure.
- Data Science and Machine Learning. With libraries such as NumPy, Pandas, Scikit-learn, and TensorFlow, Python is the de facto language for data analysis, manipulation, visualization, and building complex machine learning models. "Python for data science" is a massive field.
- Artificial Intelligence(AI). The advanced capabilities of Python, combined with its specialized AI libraries, position it as a leader in developing AI applications, including natural language processing, computer vision, and predictive analytics. "Python for artificial intelligence" is driving innovation across industries.
- Automation and Scripting. Python's simplicity and rich ecosystem make it ideal for automating repetitive tasks, system administration, and creating scripts for various purposes.
- Scientific and Numeric Computing. Researchers and scientists leverage Python for complex calculations, simulations, and data processing in fields like physics, biology, and engineering.
- Game Development. While not its primary domain, Python can be used for game development, particularly for prototyping and simple games, often with libraries like Pygame.
- DevOps. Python plays a crucial role in DevOps for scripting automation, infrastructure as code, and integrating various tools and systems.
These "python computer language examples" only scratch the surface of what's possible. Its ease of learning and deployment makes it suitable for projects of all sizes and complexities.
How Does Python Compare to Other Programming Languages?
Understanding "python vs other programming languages" is crucial for making informed decisions about which tool to use for a specific project. While Python excels in many areas, other languages have their own strengths.
- Python vs. Java. Python is generally faster to write and easier to read, making it preferable for rapid development and scripting. Java, however, often offers better performance for large-scale enterprise applications due to its compiled nature and strong typing. Java's maturity in the enterprise space is also a factor.
- Python vs. C++. C++ provides closer access to hardware and offers superior performance for systems programming, game engines, and high-performance computing. Python, on the other hand, prioritizes development speed and ease of use, making it ideal for applications where raw speed isn't the absolute top priority.
- Python vs. JavaScript. JavaScript is the language of the web browser, essential for frontend development. While Python is used for backend web development, it cannot directly run in a browser. For full-stack development, they often complement each other, with JavaScript handling the client-side and Python the server-side.
- Python vs. R. Both are popular for data science. R has a strong focus on statistical analysis and visualization, with a vast ecosystem of statistical packages. Python offers more general-purpose programming capabilities and is favored for integrating data science into larger applications and for machine learning.
Ultimately, the choice of "computer languages python" or another depends on project requirements, performance needs, and developer familiarity. Python's ability to span multiple domains with relatively low overhead makes it a highly attractive option for diverse teams and projects.
How RhodeCode Enhances Your Python Development Workflow
At RhodeCode, we understand the critical role that efficient Source control management plays in modern software development, especially when working with a powerful language like Python. While Python itself provides incredible flexibility, managing large-scale projects, collaborating effectively, and ensuring code integrity requires robust tools.
RhodeCode provides a comprehensive platform that integrates seamlessly with your Python development lifecycle. Our solutions offer advanced features for managing repositories, code reviews, and team collaboration, ensuring that your Python projects are developed and deployed with the highest standards of quality and efficiency. For enterprises, our Enterprise Features are specifically designed to address complex organizational needs, providing scalable and secure solutions for even the most demanding Python environments. Whether you're working with a small team or a large distributed workforce, RhodeCode streamlines your development workflow, allowing your developers to focus on writing great Python code rather than grappling with complex version control issues. We pride ourselves on offering a uniquely integrated experience that goes beyond basic version control.
Best Practices for Maximizing Python's Potential in 2026
To truly leverage the "python programming language" in 2026, adopting best practices is essential. These guidelines will help ensure your Python code is efficient, maintainable, and scalable.
- Adhere to PEP 8. Python Enhancement Proposal 8 (PEP 8) outlines style guidelines for Python code. Following it ensures readability and consistency across projects, making collaboration smoother.
- Use Virtual Environments. For every project, create a virtual environment (venv). This isolates project dependencies, preventing conflicts between different projects and ensuring reproducible builds.
- Write Clean, Modular Code. Break down complex problems into smaller, manageable functions and modules. This enhances readability, reusability, and makes debugging significantly easier.
- Implement Robust Testing. Write unit tests for your code. Testing frameworks like unittest or pytest help catch bugs early and ensure code reliability as your project evolves.
- Utilize Type Hinting. Python 3.5 introduced type hints, which can improve code clarity, enable better static analysis, and reduce errors, especially in larger codebases.
- Optimize for Performance (When Necessary). While Python is not the fastest language, you can optimize critical sections using techniques like C extensions, just-in-time compilers (e.g., PyPy), or leveraging optimized libraries (e.g., NumPy for numerical operations).
By embracing these best practices, you can unlock the full potential of "python features and benefits," creating robust, scalable, and maintainable applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Is Python difficult to learn for someone with no programming experience?
A1: No, Python is widely considered one of the easiest programming languages to learn, especially for beginners. Its clear syntax and focus on readability significantly reduce the learning curve. Many resources for "python for beginners" are available.
Q2: Can Python be used for mobile app development?
A2: While Python is not a primary language for native mobile app development (which typically uses Java/Kotlin for Android and Swift/Objective-C for iOS), frameworks like Kivy and BeeWare allow you to create cross-platform mobile applications with Python.
Q3: How does Python's performance compare to compiled languages?
A3: Generally, Python is slower than compiled languages like C++ or Java because it's an interpreted language. However, for most applications, especially those involving I/O operations or where development speed is crucial, Python's performance is more than adequate. For performance-critical sections, Python can integrate with C/C++ modules.
Q4: What are some popular IDEs for Python development?
A4: Popular IDEs for Python include PyCharm, VS Code (with the Python extension), Sublime Text, and Jupyter Notebook (especially for data science). These tools offer features like debugging, syntax highlighting, and code completion.
Q5: Is Python suitable for large-scale enterprise applications?
A5: Absolutely. Many large enterprises use Python for various components, including web services, data processing pipelines, and automation. Its scalability and maintainability, combined with frameworks like Django, make it a strong choice for enterprise-level solutions.
Ready to Elevate Your Python Development?
Python's journey from a niche scripting language to a dominant "computer language" is a testament to its adaptability, robust ecosystem, and vibrant community. For developers and organizations alike, mastering Python offers a competitive edge in an ever-evolving technological landscape.
Ready to streamline your Python development workflow, enhance collaboration, and ensure the highest quality for your projects?
Explore RhodeCode's advanced Source control management solutions and unlock the full potential of your team.
With our Enterprise Features, you can confidently tackle complex Python projects, scale your operations, and maintain impeccable code integrity.
Dive deeper into Python's capabilities:
- The State of Developer Ecosystem 2023 - Python Trends
- Python Developers Survey 2021 Results
- The official Python documentation